Empower Your Journey: 40 Tips for Weight Loss Triumph
Guide To Better Losses
The Guide to Better Losses, packed with essential facts, aids counselors in evaluating and troubleshooting areas of the Quick Weight Loss Program to ensure adherence and optimal weight loss results.
If you are not working with a counselor (which is highly recommended), you might find these guidelines helpful in monitoring your own weight loss.
Diet Adherence
Are You Staying Committed to Your Diet?
- Are you consistently following the correct diet plan?
- Have you recorded all required foods in your meal plan?
- Are your meal entries accurate in your diary?
- Do you weigh and measure your daily food portions diligently?
- Have you incorporated fruits between meals as suggested?
- Are you meeting your daily nutrient supplement goals?


Healthy Eating Habits
Cultivating Healthy Eating Habits
- Are you mindful about not overindulging in nutrient bars?
- Do you avoid consuming nutrient bars late in the evening?
- Is your Meal Replacement measured accurately?
- Are you staying hydrated with 80 oz of water daily?
- Do you consistently take your required vitamins?
- Are you timing your weigh-ins correctly?
- Do you keep up with regular weigh-ins?
- Is your diary comprehensive for regular evaluation?
- Have you considered variations in clothing weight?
Food Choices and Preparation
Smart Food Choices and Preparation
- Do you check canned tuna (water-packed) weekly?
- Are you opting for 40-calorie bread slices?
- Is your cottage cheese consistently 1% fat?
- Are you adhering to any red meat consumption limits?
- Have you diversified your food selections?
- Do you avoid late-night dinner meals?
- Do you remove bones and skin from meat and poultry before weighing?
- Do you trim visible fat from meat and poultry before weighing?
- Are you limiting artificial sweeteners to three packets daily?
- Is salad dressing usage limited to two tablespoons daily?
- Are you exclusively using fresh, ground turkey breast?


Lifestyle and Wellness
Balancing Lifestyle and Wellness
- Are you avoiding luncheon meats or deli/counter meats?
- Have you refrained from consuming mock crab, lobster, or shrimp?
- Do you carefully check seasonings used in your meals?
- Are you mindful of fats and cooking oils in your food prep?
- Do you approach restaurant meals mindfully?
- Have you considered any new medications or recent changes?
- Are your bowel movements regular and healthy?
- Do you acknowledge the impact of sleep and stress on water retention?
- Have you assessed changes in your activity level?
- Are you avoiding recent deviations from your prescribed plan?
Mindful Consumption
Smart and Mindful Consumption Habits
- Do you include canned fruits or veggies in your diet?
- Are you mindful of gums, mints, or juices consumption?
- Have you stopped taste-testing while cooking?
- Are you keeping an eye on diet soda and added fruit juices in your beverages?
- Are you excluding cream or artificial creamers from your coffee?

Balanced Nutrition: Embracing Three Meals a Day
Nourish Your Body with Regular Eating Habits
Eat at Least Three Meals a Day to Keep Hunger Away
The key to eliminating hunger is to eat three meals a day and several snacks spaced throughout the day. Our goal is to educate and teach our clients the benefits of eating at least three meals a day. When clients eat fewer meals, they are more likely to have more body fat, gain more weight (or lose less), and have higher blood cholesterol levels. They are also likely to consume more fat, fewer essential vitamins and minerals, and less dietary fiber.
Breakfast: Encourage them not to skip breakfast! We cannot stress enough the importance of breakfast. If they are not a breakfast eater, tell them to stop cheating themselves. The major purpose of breakfast is to break their overnight fast. Our body has its own cyclical internal rhythm. While you sleep, your body’s metabolism turns way down in preparation for 6-8 hours of no food or activity. When you wake and get started on a new day, you must have breakfast to turn on your metabolic switch moving your body’s rhythm from low ebb to high tide. Studies show that people who skip breakfast have a metabolic rate of 4% – 5% below normal. Breakfast should include some form of protein: supplement, egg, cottage cheese, or meat. It does not have to be a large meal.
Lunch
Too often skipped or overindulged, lunch boosts stamina, reduces PM slumps, and affects weight control. Here are some rules you can suggest to clients to follow for a healthful lunch: Have them establish a regular lunch hour. The brain and body function best when “fueled” at regular intervals. If they skip lunch or eat erratically, they may need about three weeks to “reset” their hunger clock, so that their appetite “rises” before a meal and “shuts down” afterward. Encourage our clients to eat a variety of foods at lunch. The trouble with eating a single food like a salad is that it does not promote lasting fullness and may lead to mineral deficiency.
Dinner
A good rule of thumb about dinner is to have them consume about 2/3 of the day’s food by late afternoon leaving 1/3 for their dinner or snack. It will take some planning for them during the day to ensure their last meal is at least three hours before bedtime. This is the time needed for food to leave the stomach and be assimilated and used by our body.
Snacks
Recognize that even an “ideal” breakfast or lunch can’t always prevent amidmorning or 4:00 PM slump. Snacking on a fruit or a supplement, or going for a 5-minute walk is a far better solution than both sugar and coffee that can cause moodswings.

Calories
There are three (3) main sources of calories. Carbohydrates, Fats, and Proteins are the primary sources of energy to the body because they supply fuel necessary for body heat and work. The fuel is expressed in calories, a term that signifies the amount of energy to be released when food is metabolized. Therefore, foods high in energy are high in calories. While foods low in energy are low in calories.
Perhaps you have read that the consumption of 3,500 calories is required to create one pound of fat. That is the figure generally used.
If you overeat by 100 calories a day, then you will gain about 1 lb. every 35 days. If you eat 100 calories less than required to meet your daily needs, you will lose 1 lb. per month. But, suppose you go on eating those 100 extra calories a day, not for one month, but for one year. You will have gained 12 Ibs., that’s 240 Ibs. in 20 years.
It is important to realize that this cycle of weight gain can be initiated by a decrease in activity or an increase in calories.
However, all calories are not alike. Calories from fat help make you fatter. Fat in food has a profile that is already similar to that of fat found in your body. This makes fat calories prone to storage in those problem areas. It’s very easy to eat 100 calories in fat(that is one tablespoon of butter or oil). You can absorb that amount of fat in French Fries. These fats, also known as cholesterol, are well known factors in heart disease.
It is crucial that our client’s follow our program precisely, because all calories are notcreated equally. We are not a calorie counting diet, but more of a chemically balanceddiet, which contains a mixture of protein, fat and carbohydrate calories. This will ensurethe safest and most effective weight loss possible.

Transformation Spotlight
Health Facts about Obesity
We are built from the food we eat, and approximately 60% of all Americans are overweight. The vast majority of overweight persons are so because they simply do not burn up the fuel they take in. but there are rare circumstances in which abnormalities in metabolism lead to uncontrolled storage of fat. It takes approximately 3,500 excess calories (more food or drink taken in than burned off in exercise) for most people to develop one extra pound of fat.
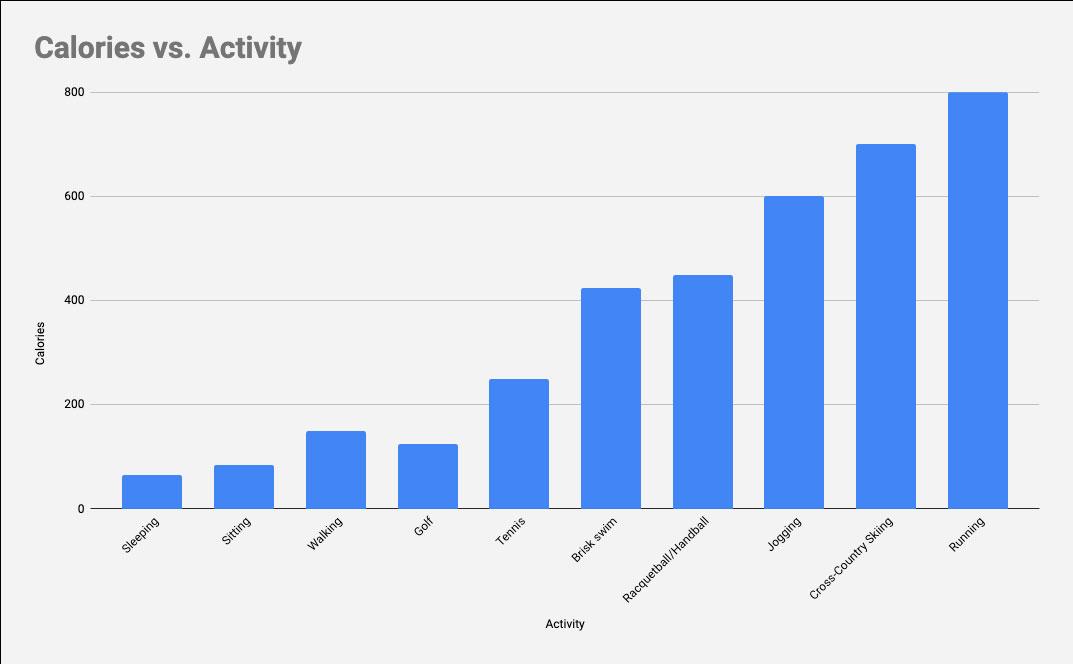
Calories Used Per Hour With Exercise
Types Of Obesity
Obesity, often stemming from excessive food consumption, tends to distribute itself across the entire body. This form of obesity is referred to as exogenous obesity. In contrast, hormonal imbalances lead to endogenous obesity, resulting in a distinct and uneven appearance, such as a substantial hip size coupled with a slender upper body.
Childhood obesity gives rise to a notable surge in the overall count of fat cells. An overweight child could mature into an adult burdened with an excess of 50 billion fat cells. These individuals grapple with a persistent struggle to manage their weight throughout their lives.
On the other hand, adult-onset obesity is more prevalent and manifests not as a proliferation of fat cells, but rather as an enlargement of the existing cells.
Types Of Obesity
Obesity, often stemming from excessive food consumption, tends to distribute itself across the entire body. This form of obesity is referred to as exogenous obesity. In contrast, hormonal imbalances lead to endogenous obesity, resulting in a distinct and uneven appearance, such as a substantial hip size coupled with a slender upper body.
Childhood obesity gives rise to a notable surge in the overall count of fat cells. An overweight child could mature into an adult burdened with an excess of 50 billion fat cells. These individuals grapple with a persistent struggle to manage their weight throughout their lives.
On the other hand, adult-onset obesity is more prevalent and manifests not as a proliferation of fat cells, but rather as an enlargement of the existing cells.
Relative Increase of Diseases with Obesity
Many diseases are associated with obesity. If a person is 25% overweight, the death rate is 1.7 times normal. For those 40% overweight, the death rate increases to 2.2 times normal.
Hypertension
Approximately 25 million Americans suffer from high blood pressure, and obesity is one of the chief factors for its occurrence. Extra fat puts an added strain on the entire circulatory system, leading to high blood pressure, strokes, heart attacks, and many other problems.
Arteriosclerosis
Hardening of the arteries, known medically as arteriosclerosis, is a disease of aging, but can sometimes be seen in obese children as young as 5 or 6 years of age. Yellowish-white plaques with cholesterol and calcium deposits cause these arteries to become rigid and result in high blood pressure, heart attacks, and strokes.
Angina Pectoris
Angina pectoris literally means “strangling of the chest.” It is caused by a temporary insufficiency in blood supply to the heart muscle itself. Symptoms include a feeling of a heavy weight over the chest, pain extending to the chest and arms (especially in the left), and relief with rest. Common precipitating factors of angina pectoris in obese patients include heavy meals, exertion, colds, and smoking.
Myocardial Infarction
Heart attacks are the leading cause of death in the United States. A heart attack occurs when one of the coronary arteries taking blood to the heart muscle is clogged with a blood clot or cholesterol plaque, and the heart muscle is deprived of sufficient nutrition. Over one-half of all patients suffering a first heart attack die before even reaching the hospital. Obesity is one of the leading causes of heart attacks.
Stroke
Strokes are caused by bleeding or blood clots occurring within the brain. Approximately two-thirds of all strokes are caused by clotting, and one-third by hemorrhaging. Obesity, hypertension, and arteriosclerosis are leading causes of strokes. Strokes produce paralysis, usually on one side of the body, speech defects, mental impairment, and often death.
Fatty Heart
The excessive amounts of yellow fat almost totally covering the obese heart will predispose the heart to hardening of the arteries and heart attacks. Obese persons literally smother their hearts with excessive fat tissue.
Fatty Liver
Fatty liver is a condition in which there are excessive deposits of fat in the liver cells coloring the liver yellow. It is associated with a variety of problems, including alcoholism, obesity, diabetes, certain anemic problems, and chronic infections. There is no specific treatment for fatty liver, except to control the problems causing it, such as alcoholism or nutritional abnormalities.
Gallstones
Gallstones occur in approximately 15% of the adult population and are particularly prone to be seen in obese middle-aged women. Gallstones may produce symptoms of indigestion, bloating, and abdominal pains. If the stones obstruct drainage of bile from the gallbladder or liver, severe pain and gallbladder inflammation will result, requiring emergency surgery.
Fatty Kidney
Obesity not only causes large deposits of fat tissue in the kidneys, but it also leads to hypertension and degenerative changes within the kidneys. These degenerative changes associated with obesity, arteriosclerosis, and hypertension will eventually lead to kidney failure.
Diabetes
Over 10 million Americans suffer from diabetes, more than 20% of these persons don‘t know they have the disease, and more than 80% of adult diabetics are overweight before the disease develops. Most people are at least 15% too heavy when they develop diabetes. Maintaining proper weight is frequently the only way to prevent diabetes in middle-aged and older persons.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Few people associate obesity with blindness, but because of the high percentage of diabetes related to obesity, there is actually a definite link between the two. Diabetes is the leading cause of blindness in America. Diabetics are prone to develop tiny hemorrhages in the retina of the eye, known as diabetic retinopathy. Areas of past bleeding may be seen as white, irregular scars intermixed with areas of recent bleeding. There is no specific treatment for diabetic retinopathy other than weight control and management of the diabetes itself.
Varicose Veins
Permanently distended and tortuous veins are a problem often associated with obesity. They result from excessive loads on the vascular system, particularly in the legs. These distended veins are very susceptible to injury, resulting in skin sores known as stasis ulcers. Deep erosions of these ulcers may eventually lead to gangrene and the necessity for amputation.
Hemorrhoids
Dilated varicose veins of the lower portion of the rectum and anus are known as hemorrhoids. These ballooned-out veins result from excessive pressure on the venous drainage system, and are associated with obesity, pregnancy and constipation. If these veins become swollenand filled with clotted blood, considerable pain occurs and eventually surgerymay be necessary.
Degenerative Arthritis of Hip
Degenerative arthritis is a wearing-out process of a joint. Obesity is a major contributingfactor to this problem because overweight persons may carry excessive loads on their joints, particularly the hips and knees. The articular surfaces of these joints become ragged and scarred with calcium and bony deposits. Any type of movement becomes very painful.Treatment involves weight reduction, avoidance of unnecessary stress, and sometimessurgical replacement of the diseased joint with an artificial joint.
Degenerative Arthritis of Knee
Chronic pain and swelling of the knees is commonly seen in older obese persons. Thiscondition can be greatly relieved through weight reduction and proper use of a cane to remove some stress from the knees during walking. Surgical replacement with an artificial kneejoint is necessary in severe cases.
Degenerative Arthritis of Hip
Degenerative arthritis is a wearing-out process of a joint. Obesity is a major contributing factor to this problem because overweight persons may carry excessive loads on their joints, particularly the hips and knees. The articular surfaces of these joints become ragged and scarred with calcium and bony deposits. Any type of movement becomes very painful. Treatment involves weight reduction, avoidance of unnecessary stress, and sometimes surgical replacement of the diseased joint with an artificial joint.
Degenerative Arthritis of Knee
Chronic pain and swelling of the knees is commonly seen in older obese persons. Thiscondition can be greatly relieved through weight reduction and proper use of a cane to remove some stress from the knees during walking. Surgical replacement with an artificial kneejoint is necessary in severe cases.
Calories Used Per Hour With Exercise
Types Of Obesity
Obesity, often stemming from excessive food consumption, tends to distribute itself across the entire body. This form of obesity is referred to as exogenous obesity. In contrast, hormonal imbalances lead to endogenous obesity, resulting in a distinct and uneven appearance, such as a substantial hip size coupled with a slender upper body.
Childhood obesity gives rise to a notable surge in the overall count of fat cells. An overweight child could mature into an adult burdened with an excess of 50 billion fat cells. These individuals grapple with a persistent struggle to manage their weight throughout their lives.
On the other hand, adult-onset obesity is more prevalent and manifests not as a proliferation of fat cells, but rather as an enlargement of the existing cells.
Types Of Obesity
Obesity, often stemming from excessive food consumption, tends to distribute itself across the entire body. This form of obesity is referred to as exogenous obesity. In contrast, hormonal imbalances lead to endogenous obesity, resulting in a distinct and uneven appearance, such as a substantial hip size coupled with a slender upper body.
Childhood obesity gives rise to a notable surge in the overall count of fat cells. An overweight child could mature into an adult burdened with an excess of 50 billion fat cells. These individuals grapple with a persistent struggle to manage their weight throughout their lives.
On the other hand, adult-onset obesity is more prevalent and manifests not as a proliferation of fat cells, but rather as an enlargement of the existing cells.
Relative Increase of Diseases with Obesity
Many diseases are associated with obesity. If a person is 25% overweight, the death rate is 1.7 times normal. For those 40% overweight, the death rate increases to 2.2 times normal.
Hypertension
Approximately 25 million Americans suffer from high blood pressure, and obesity is one of the chief factors for its occurrence. Extra fat puts an added strain on the entire circulatory system, leading to high blood pressure, strokes, heart attacks, and many other problems.
Arteriosclerosis
Hardening of the arteries, known medically as arteriosclerosis, is a disease of aging, but can sometimes be seen in obese children as young as 5 or 6 years of age. Yellowish-white plaques with cholesterol and calcium deposits cause these arteries to become rigid and result in high blood pressure, heart attacks, and strokes.
Angina Pectoris
Angina pectoris literally means “strangling of the chest.” It is caused by a temporary insufficiency in blood supply to the heart muscle itself. Symptoms include a feeling of a heavy weight over the chest, pain extending to the chest and arms (especially in the left), and relief with rest. Common precipitating factors of angina pectoris in obese patients include heavy meals, exertion, colds, and smoking.
Myocardial Infarction
Heart attacks are the leading cause of death in the United States. A heart attack occurs when one of the coronary arteries taking blood to the heart muscle is clogged with a blood clot or cholesterol plaque, and the heart muscle is deprived of sufficient nutrition. Over one-half of all patients suffering a first heart attack die before even reaching the hospital. Obesity is one of the leading causes of heart attacks.
Stroke
Strokes are caused by bleeding or blood clots occurring within the brain. Approximately two-thirds of all strokes are caused by clotting, and one-third by hemorrhaging. Obesity, hypertension, and arteriosclerosis are leading causes of strokes. Strokes produce paralysis, usually on one side of the body, speech defects, mental impairment, and often death.
Fatty Heart
The excessive amounts of yellow fat almost totally covering the obese heart will predispose the heart to hardening of the arteries and heart attacks. Obese persons literally smother their hearts with excessive fat tissue.
Fatty Liver
Fatty liver is a condition in which there are excessive deposits of fat in the liver cells coloring the liver yellow. It is associated with a variety of problems, including alcoholism, obesity, diabetes, certain anemic problems, and chronic infections. There is no specific treatment for fatty liver, except to control the problems causing it, such as alcoholism or nutritional abnormalities.
Gallstones
Gallstones occur in approximately 15% of the adult population and are particularly prone to be seen in obese middle-aged women. Gallstones may produce symptoms of indigestion, bloating, and abdominal pains. If the stones obstruct drainage of bile from the gallbladder or liver, severe pain and gallbladder inflammation will result, requiring emergency surgery.
Fatty Kidney
Obesity not only causes large deposits of fat tissue in the kidneys, but it also leads to hypertension and degenerative changes within the kidneys. These degenerative changes associated with obesity, arteriosclerosis, and hypertension will eventually lead to kidney failure.
Diabetes
Over 10 million Americans suffer from diabetes, more than 20% of these persons don‘t know they have the disease, and more than 80% of adult diabetics are overweight before the disease develops. Most people are at least 15% too heavy when they develop diabetes. Maintaining proper weight is frequently the only way to prevent diabetes in middle-aged and older persons.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Few people associate obesity with blindness, but because of the high percentage of diabetes related to obesity, there is actually a definite link between the two. Diabetes is the leading cause of blindness in America. Diabetics are prone to develop tiny hemorrhages in the retina of the eye, known as diabetic retinopathy. Areas of past bleeding may be seen as white, irregular scars intermixed with areas of recent bleeding. There is no specific treatment for diabetic retinopathy other than weight control and management of the diabetes itself.
Varicose Veins
Permanently distended and tortuous veins are a problem often associated with obesity. They result from excessive loads on the vascular system, particularly in the legs. These distended veins are very susceptible to injury, resulting in skin sores known as stasis ulcers. Deep erosions of these ulcers may eventually lead to gangrene and the necessity for amputation.
Hemorrhoids
Dilated varicose veins of the lower portion of the rectum and anus are known as hemorrhoids. These ballooned-out veins result from excessive pressure on the venous drainage system, and are associated with obesity, pregnancy and constipation. If these veins become swollenand filled with clotted blood, considerable pain occurs and eventually surgerymay be necessary.
Degenerative Arthritis of Hip
Degenerative arthritis is a wearing-out process of a joint. Obesity is a major contributingfactor to this problem because overweight persons may carry excessive loads on their joints, particularly the hips and knees. The articular surfaces of these joints become ragged and scarred with calcium and bony deposits. Any type of movement becomes very painful.Treatment involves weight reduction, avoidance of unnecessary stress, and sometimessurgical replacement of the diseased joint with an artificial joint.
Degenerative Arthritis of Knee
Chronic pain and swelling of the knees is commonly seen in older obese persons. Thiscondition can be greatly relieved through weight reduction and proper use of a cane to remove some stress from the knees during walking. Surgical replacement with an artificial kneejoint is necessary in severe cases.
Degenerative Arthritis of Hip
Degenerative arthritis is a wearing-out process of a joint. Obesity is a major contributing factor to this problem because overweight persons may carry excessive loads on their joints, particularly the hips and knees. The articular surfaces of these joints become ragged and scarred with calcium and bony deposits. Any type of movement becomes very painful. Treatment involves weight reduction, avoidance of unnecessary stress, and sometimes surgical replacement of the diseased joint with an artificial joint.
Degenerative Arthritis of Knee
Chronic pain and swelling of the knees is commonly seen in older obese persons. Thiscondition can be greatly relieved through weight reduction and proper use of a cane to remove some stress from the knees during walking. Surgical replacement with an artificial kneejoint is necessary in severe cases.

Enhance Your Weight Loss Journey
Satisfy Cravings, Boost Metabolism
Discover snacks that satisfy cravings and support your metabolism goals. Explore our snacks category to find nourishing options that enhance your healthy lifestyle. Click ‘Buy Now’ to start your flavorful journey.
